They say money doesn’t grow on trees, but a nearly 75,000-acre swath of redwood and fir forests blanketing the wildlands of Sonoma and Mendocino counties is generating millions of dollars as it contributes to California’s ambitious campaign to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
In a reversal of forest profiteering that dates back to the mid-1800s, the trees are making landowners money by staying upright and growing fast on damp coastal hills where vegetation thrives and few humans set foot.
The Conservation Fund, a Virginia-based nonprofit, has since 2008 sold more than $36 million worth of a new forest commodity called carbon credits, also known as carbon offsets, which represent 4 million metric tons of greenhouse gases sequestered, or stored, by forests that in turn must be sustained for 100 years.
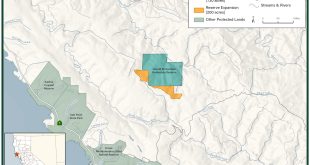
More than $2 million in credits have already sold for the former Preservation Ranch, a 19,645-acre property in northwestern Sonoma County that once was the focus of an intense environmental controversy.
Purchased by the fund for $24.5 million in public and private funding in 2013 — in the largest conservation deal by acreage in county history — the ranch, renamed Buckeye Forest, is forever protected against a future that once included a proposed 1,800 acre forest-to-vineyard conversion. Those plans aroused environmentalists’ anger and would have eliminated more than 300,000 trees.
Now the redwoods in the remote Buckeye tract, which lies east of Annapolis and stretches from Skaggs Springs Road to the Mendocino County line, are doing what comes naturally by absorbing carbon dioxide, the primary contributor to global warming.
 Friends of Gualala River Protecting the Gualala River watershed and the species living within it
Friends of Gualala River Protecting the Gualala River watershed and the species living within it